ASTM A325 bolts are high-strength structural bolts used in steel-to-steel connections, particularly in buildings, bridges, and other heavy construction projects. These bolts are designed for structural applications where high load capacity and durability are required.
Unlike other ASTM grades, A325 is specific not only in the chemical and mechanical requirements, but also in the allowed configuration. These bolts range in diameter from 1/2″ through 1-1/2″ and are manufactured from a medium-carbon or medium-carbon alloy steel that is quenched and tempered to develop the desired mechanical properties.
Product Picture Display

What does A325 mean on a bolt?
The designation A325 on a bolt refers to the ASTM A325 specification, which defines a type of high-strength structural bolt commonly used in steel-to-steel connections for buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
Key Characteristics of ASTM A325 Bolts
High Strength:
Made from medium carbon steel, carbon boron steel, or medium carbon alloy steel
Minimum tensile strength: 120,000 psi (for diameters ≤ 1 inch)
Minimum yield strength: 92,000 psi
Heat Treatment:
Bolts are quenched and tempered to enhance strength and toughness.
Threading:
Standard threading is Unified National Coarse (UNC), unless specified otherwise.
Identification Markings:
A325 is stamped on the bolt head along with the manufacturer’s mark.
Type 1 or Type 3 variations may have additional markings to differentiate them.
Types
| TYPE 1 | Medium carbon, carbon boron, or medium carbon alloy steel. |
| TYPE 2 | Withdrawn November 1991. |
| TYPE 3 | Weathering steel. |
| T | Fully threaded A325. (Restricted to 4 times the diameter in length) |
| M | Metric A325. |
What is the difference between ASTM A325 type 1 and type 3?
| Feature | ASTM A325 Type 1 | ASTM A325 Type 3 |
| Material | Medium carbon steel, carbon boron steel, or medium carbon alloy steel | Weathering steel (corrosion-resistant steel) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Standard corrosion resistance; often requires galvanizing for protection | High corrosion resistance due to the formation of a protective oxide layer (similar to Corten steel) |
| Appearance | Silver/gray when galvanized or plain black | Reddish-brown patina due to weathering steel properties |
| Coating Options | Can be galvanized (hot-dip, mechanical, or electroplated) | Not recommended for galvanizing (it affects weathering properties) |
| Common Applications | General structural connections, bridges, buildings | Outdoor structures, bridges, exposed steel applications |
| Equivalent Material | Similar to ASTM A490 (high-strength bolts) | Similar to ASTM A588 (weathering steel) |
ASTM A325 bolts are high-strength structural bolts commonly used in steel-to-steel connections in construction and infrastructure. The main difference between Type 1 and Type 3 lies in their material composition and corrosion resistance.
Which One Should You Use?
Use Type 1 if the bolts will be galvanized or painted for corrosion protection.
Use Type 3 if the bolts are in an outdoor environment where natural weathering is preferred over coating.
Connection type of ASTM A325 Bolts
| SC | Slip critical connection. |
| X | Bearing-type connection with threads excluded from the shear plane. |
| N | Bearing type connection with threads included in the shear plane. |
ASTM A325 Bolt Chemical Composition
| Type 1 Bolts | ||||
| Element | Carbon Steel | Carbon Boron Steel | Alloy Steel | Alloy Boron Steel |
| Carbon | 0.30 – 0.52% | 0.30 – 0.52% | 0.30 – 0.52% | 0.30 – 0.52% |
| Manganese, min | 0.60% | 0.60% | 0.60% | 0.60% |
| Phosphorus, max | 0.04% | 0.04% | 0.04% | 0.04% |
| Sulfur, max | 0.05% | 0.05% | 0.04% | 0.04% |
| Silicon | 0.15-0.30% | 0.10 – 0.30% | 0.15 – 0.35% | 0.15 – 0.35% |
| Boron | 0.0005 – 0.003% | 0.0005 – 0.003% | ||
| Alloying Elements | * | * | ||
ASTM A325 Bolt Mechanical Properties
| Size | Tensile, ksi | Yield, ksi | Elong. %, min | RA %, min |
| 1⁄2 – 1 | 120 min | 92 min | 14 | 35 |
| 11⁄8 – 11⁄2 | 105 min | 81 min | 14 | 35 |
Recommended Nuts and Washers
| Nuts | Washers | |||
| Type 1 | Type 3 | Type 1 | Type 3 | |
| Plain | Galvanized | Plain | ||
| A563C, C3, D, DH, DH3 | A563DH | A563C3, DH3 | F436-1 | F436-3 |
ASTM A325 Bolt Dimensions
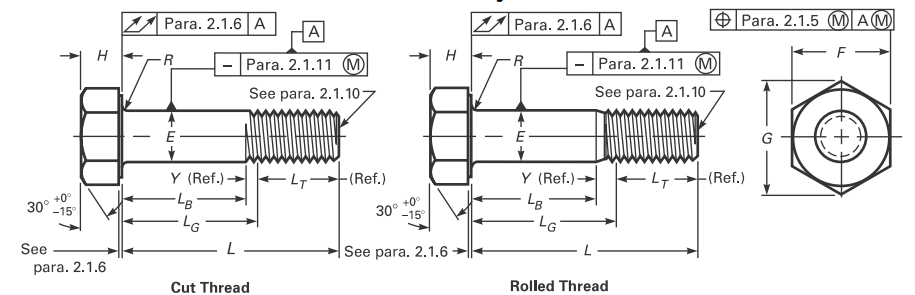
| Bolt Diameter | D | F | C | H | T | |||||
| Body Diameter | Width Across Flats | Width Across Corners | Height | Thread Length | ||||||
| Max | Basic | Max | Min | Max | Min | Basic | Max | Min | Basic | |
| 1⁄2 | 0.515 | 7⁄8 | 0.875 | 0.85 | 1.01 | 0.969 | 5⁄16 | 0.323 | 0.302 | 1 |
| 5⁄8 | 0.642 | 11⁄16 | 1.062 | 1.031 | 1.227 | 1.175 | 25⁄64 | 0.403 | 0.378 | 1.25 |
| 3⁄4 | 0.768 | 11⁄4 | 1.25 | 1.212 | 1.443 | 1.383 | 15⁄32 | 0.483 | 0.455 | 1.38 |
| 7⁄8 | 0.895 | 17⁄16 | 1.438 | 1.394 | 1.66 | 1.589 | 35⁄64 | 0.563 | 0.531 | 1.5 |
| 1 | 1.022 | 15⁄8 | 1.625 | 1.575 | 1.876 | 1.796 | 39⁄64 | 0.627 | 0.591 | 1.75 |
| 11⁄8 | 1.149 | 113⁄16 | 1.812 | 1.756 | 2.093 | 2.002 | 11⁄16 | 0.718 | 0.658 | 2 |
| 11⁄4 | 1.277 | 2 | 2 | 1.938 | 2.309 | 2.209 | 25⁄32 | 0.813 | 0.749 | 2 |
| 13⁄8 | 1.404 | 23⁄16 | 2.188 | 2.119 | 2.526 | 2.416 | 27⁄32 | 0.878 | 0.81 | 2.25 |
| 11⁄2 | 1.531 | 23⁄8 | 2.375 | 2.3 | 2.742 | 2.622 | 15⁄16 | 0.974 | 0.902 | 2.25 |
Tensile Load Requirements for Bolts Tested Full-Size
Bolt Size, Threads per Inch, and Series Designation | Tensile Load,B min, lbf | Proof Load,B Length Measure- ment Method | Alternative Proof Load,B Yield Strength Method | |
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
| 1⁄2 –13 UNC | 0.142 | 17050 | 12050 | 13050 |
| 5⁄8 –11 UNC | 0.226 | 27100 | 19200 | 20800 |
| 3⁄4 –10 UNC | 0.334 | 40100 | 28400 | 30700 |
| 7⁄8 –9 UNC | 0.462 | 55450 | 39250 | 42500 |
| 1–8 UNC | 0.606 | 72700 | 51500 | 55750 |
| 11⁄8 –7 UNC | 0.763 | 80100 | 56450 | 61800 |
| 11⁄4 –7 UNC | 0.969 | 101700 | 71700 | 78500 |
| 13⁄8 –6 UNC | 1.155 | 121300 | 85450 | 93550 |
| 11⁄2 –6 UNC | 1.405 | 147500 | 104000 | 113800 |
What is the difference between A325 and A490 bolts?
1. Comparison Table: A325 vs. A490
| Feature | ASTM A325 | ASTM A490 |
| Material | Medium carbon steel, carbon boron steel, or medium carbon alloy steel | Alloy steel, quenched and tempered |
| Tensile Strength | 120 ksi (for bolts ≤ 1” diameter) | 150 ksi (higher strength) |
| Yield Strength | 92 ksi | 130 ksi |
| Coating (Galvanizing) | Can be hot-dip galvanized or mechanically galvanized | Cannot be galvanized (Risk of hydrogen embrittlement) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Requires coating for corrosion resistance | Limited (since galvanizing is not allowed) |
| Hardness | HRC 19-30 | HRC 33-39 (harder steel) |
| Fully Threaded Options | Available as A325T | Available as A490T |
| Applications | General structural connections, bridges, steel frames | High-strength applications where extra load capacity is required |
| Replacement Standard | Now classified under ASTM F3125 Grade A325 | Now classified under ASTM F3125 Grade A490 |
✅ Strength & Material:
A490 bolts are much stronger than A325 bolts due to their alloy steel composition and higher heat treatment levels.
A325 bolts are made of medium carbon steel and are slightly softer.
✅ Coating & Corrosion Resistance:
A325 bolts can be galvanized for corrosion resistance.
A490 bolts cannot be galvanized because the high-strength alloy steel is susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement, which can lead to cracking.
If corrosion resistance is needed for A490, a better alternative is weathering steel (A490 Type 3), which naturally develops a protective rust layer.
✅ Usage & Applications:
A325 bolts are commonly used for standard structural connections in buildings and bridges.
A490 bolts are preferred for high-strength applications where greater load-bearing capacity is required.
Are A325 bolts fully threaded?
No, ASTM A325 bolts are typically not fully threaded. They are partially threaded with a designated grip length (unthreaded portion) to provide maximum strength in structural connections.
However, fully threaded A325 bolts do exist but are classified under a different designation.
Standard Threading for A325 Bolts
Standard A325 Bolts (Partially Threaded)
Designed with a shank (unthreaded portion) to handle shear loads.
Commonly used in structural steel connections, where the unthreaded portion improves load-bearing capacity.
A325T (Fully Threaded)
The “T” suffix indicates a fully threaded version.
Used in applications where a full-thread design is necessary for clamping force rather than shear strength.
A325 Bolts in Shorter Lengths
For bolts ≤ 4 times the diameter, they may be fully threaded simply because of their short length.
You can get an offer for products in below material forms:
-Pipe and Tube (EN 10216-5, ASTM A213, ASTM A249, A312, A790,)
-Forged Fitting and Flange (ASTM A182 , ASTM A105,ASTM B564 )
-Butt Weld Fittings (ASTM A234, ASTM A403,ASTM A815)
-Round bar , Billet (ASTM A276, ASTM A479)
– Plate, Sheet, Strip(ASTM A240, EN 10028-7, A480)
-Bolting, Nuts(ASTM A193, A194, A320)
ASTM A325 Bolts Exported Countries
We Export ASTM A325 Bolts to Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, Oman, Kuwait, Turkey, Egypt, Yemen , Syria, Jordan, Cyprus, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, South Korea, Japan, Sri Lanka, Maldives, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Uruguay, United States Of America, Canada, Mexico, Panama, Jamaica, Bahamas, Denmark, Norway, Germany, France, Italy, United Kingdom, Spain, Belgium, Greece, Czech Republic, Portugal, Hungary, Albania, Austria, Finland, Ireland, Croatia, Malta, Nigeria, Algeria, Angola, South Africa, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, Europe, Africa, Asia, North America, South America, Middle East. etc
